
Which of These 6 Strategic Frameworks is Right For Your Business?
Last update: 23 February 2024 at 10:05 am
Any marketing plan must have a strategic foundation. They assist us in determining where we are, where we want to go, and what steps we need to take as a company to get there.
Marketers employ a variety of strategic frameworks which we will explore in this article.
What Is a Strategic Framework?
A strategic framework is a technique of organizing that explains how a project or effort will assist the organization in achieving critical goals.
It may be used to define individual marketing programs or efforts from a marketing standpoint, ensuring that they are constantly following the broader company plan.
You may utilize strategic frameworks to drive new product or service offerings or to figure out how the marketing team can assist improve revenue, for example.
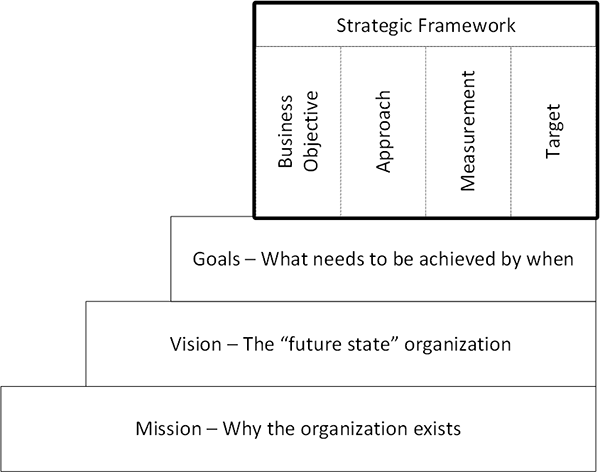
A strategic framework is made up of four parts:
- Business objective – What is the goal of the project or initiative?
- Approach – What steps will be taken to accomplish that goal?
- Measurement – How will success be assessed and reported?
- Target – What is the expected improvement that will determine whether or not you are successful?
The strategic framework must be founded on the organization’s mission, vision, and goals to be successful (MVG).
Mission statement: outlines the reason for the existence of the organization.
Vision statement: outlines what the organization aims to be in the future; it describes the organization’s “future state.”
Goals: specify what must be accomplished by a certain date, but they do not specify how those objectives will be met.
A strategic framework can help with this. The strategic framework explains how a project or initiative will contribute to the organization’s MVG.
The Advantages of Creating a Strategic Framework
The beginnings of a comprehensive communication plan are a logical result of the strategic framework. A communication plan specifies which messages will be given to which audiences, when, and in what media or format, and at what intervals.
You’ve already gotten a head start on the communication strategy by answering the WIIFM as part of the strategic framework development.
A strategic framework ensures that your project will be able to survive management changes. Let’s be honest. The management of a company changes from time to time, and new managers generally bring fresh ideas and ways of thinking to their new positions.
Does this imply that your brilliant idea or project may be postponed or canceled? To be honest, yeah! That new management will almost certainly analyze your project.
However, because a well-defined strategic framework links your project’s outcomes to the organization’s MVG, your project’s chances of being canceled are slim.
Finally, creating a strategic framework allows for business-like discussions with top management about how your project contributes to the organization’s MVG. No one will ever throw you out of their workplace for having a thoughtful and fair debate about how to help the company succeed.
6 Popular Successful Strategic Framework
We’ll go over some of the most prominent strategic planning frameworks over the last 60 years to help you decide which one is right for your company.
OGSM
Although it is commonly assumed that OGSM (short for Objectives, Goals, Strategies, and Measures) was brought to America from Japan in the 1950s and had origins in Total Quality, the exact origin of this strategic planning framework is uncertain. It is thought to have been invented under Japan’s Occupation after WWII.
The contemporary version of the OGSM framework, which transforms strategic aims and concepts into organizational behavior, is ascribed to Procter & Gamble. OGSM has been utilized by Fortune 500 organizations all over the world since it was first deployed by P&G.

OGSM provides a clear structure for designing, aligning, and executing a long-term (3-5 year) strategic plan shortly (one page). The OGSM framework connects large picture strategic components (mission, vision, and values) to operational elements (goals, strategies, initiatives, measures).
The result is a strategic plan that is thorough, robust, and actionable. Best for businesses that lack a clear strategic framework, those that have seen quick expansion (or rapid collapse), those that have recently undergone mergers and acquisitions, or any company that fails to meet its financial goals.
Ansoff Matrix
Igor Ansoff, a Russian-American, created the Ansoff Matrix, commonly known as the Ansoff Product and Market Growth Matrix. Ansoff is recognized as the “Father of Strategic Management” and is credited with the creation and articulation of strategic management as a concept.
He is a mathematician, scientist, business manager, and researcher.
Ansoff described product-market strategy as “a combined description of a product line and the associated set of missions which the goods are meant to achieve.”
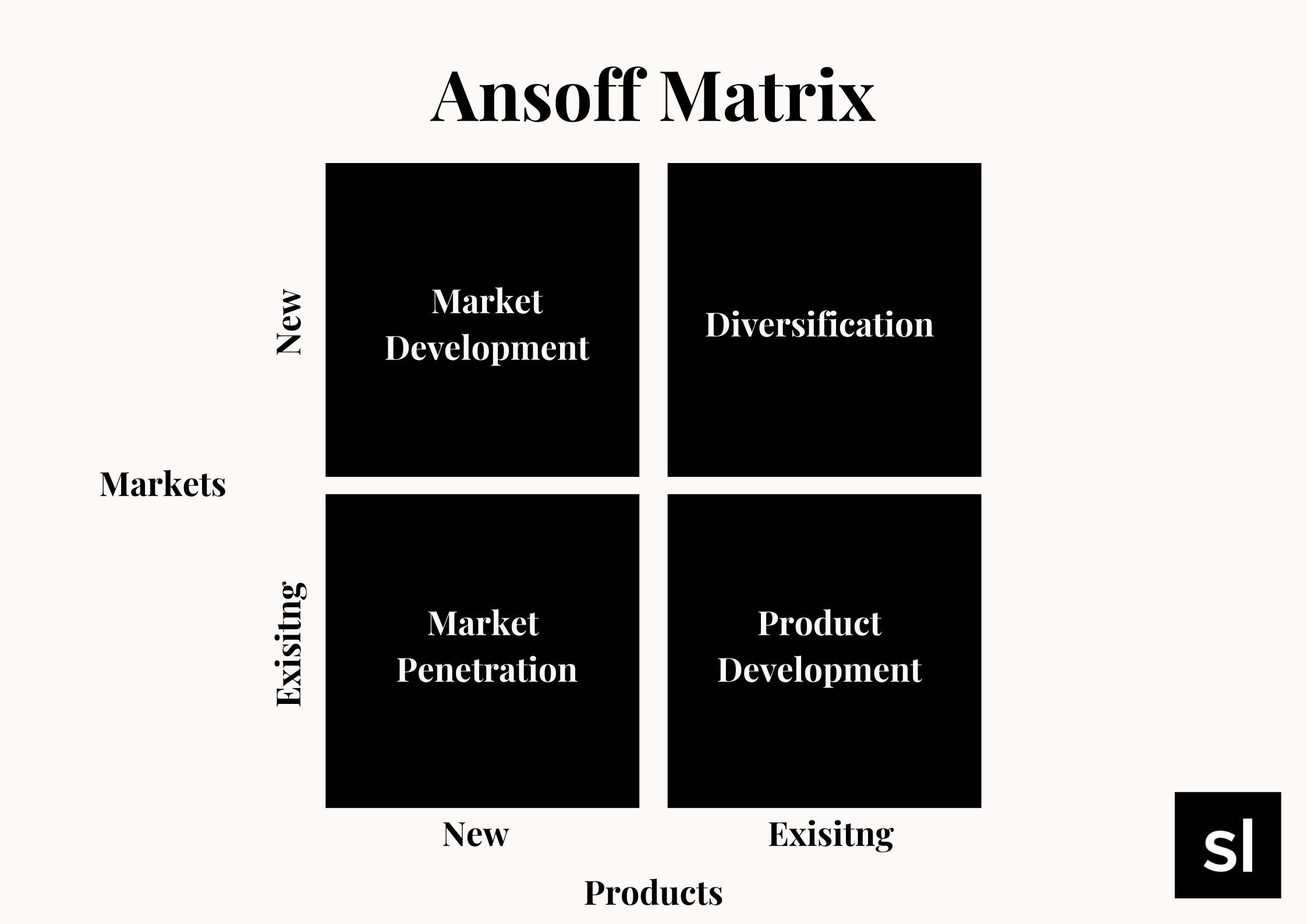
Through four marketing strategy options, the Ansoff Matrix is meant to assist businesses in determining their routes to product and market growth:
- Price, advertising, and distribution modifications increased sales of current items in existing areas, resulting in market penetration.
- Product development entails the creation of new items or the modification of current products to sell them in existing markets.
- Market development is increasing sales of current items in new markets through price, packaging, distribution, and geographic expansion.
- Diversification entails the sale of new items in new markets, either through related diversification (diversification within the same sector) or unrelated diversification (diversification outside of the same industry) (diversification in a completely new industry).
BCG Matrix
The BCG matrix (Boston Consultant Group) is a portfolio management structure that helps organizations determine which goods or services to invest in based on market growth and market share rather than market growth and share.
Market growth – how well the product is growing when compared to other products?
Market share – what is the size of the market the product has captured compared to the competition?
It’s also known as the growth-share matrix, and it’s made up of four quadrants that represent distinct product categories. The rate of market growth is represented by the y-axis, while the market share is represented by the x-axis.

When should you utilize it?
- Identifying growth possibilities by selecting where to spend and where to withdraw based on the product portfolio
- To learn which goods a company should maintain, sell, or spend more on.
- To gain a current picture of how the market’s current items are doing
7S Model
The McKinsey 7S Framework is based on the idea that success requires seven internal organizational aspects to be in sync. These factors are classified as “hard elements,” which are easier to identify and affect, and “soft elements,” which are more difficult to describe and control.
The model’s design is designed to assist businesses in determining which aspects need to be changed to attain/maintain alignment or achieve a higher degree of performance.
Strategy, structure, and systems are the hard aspects.
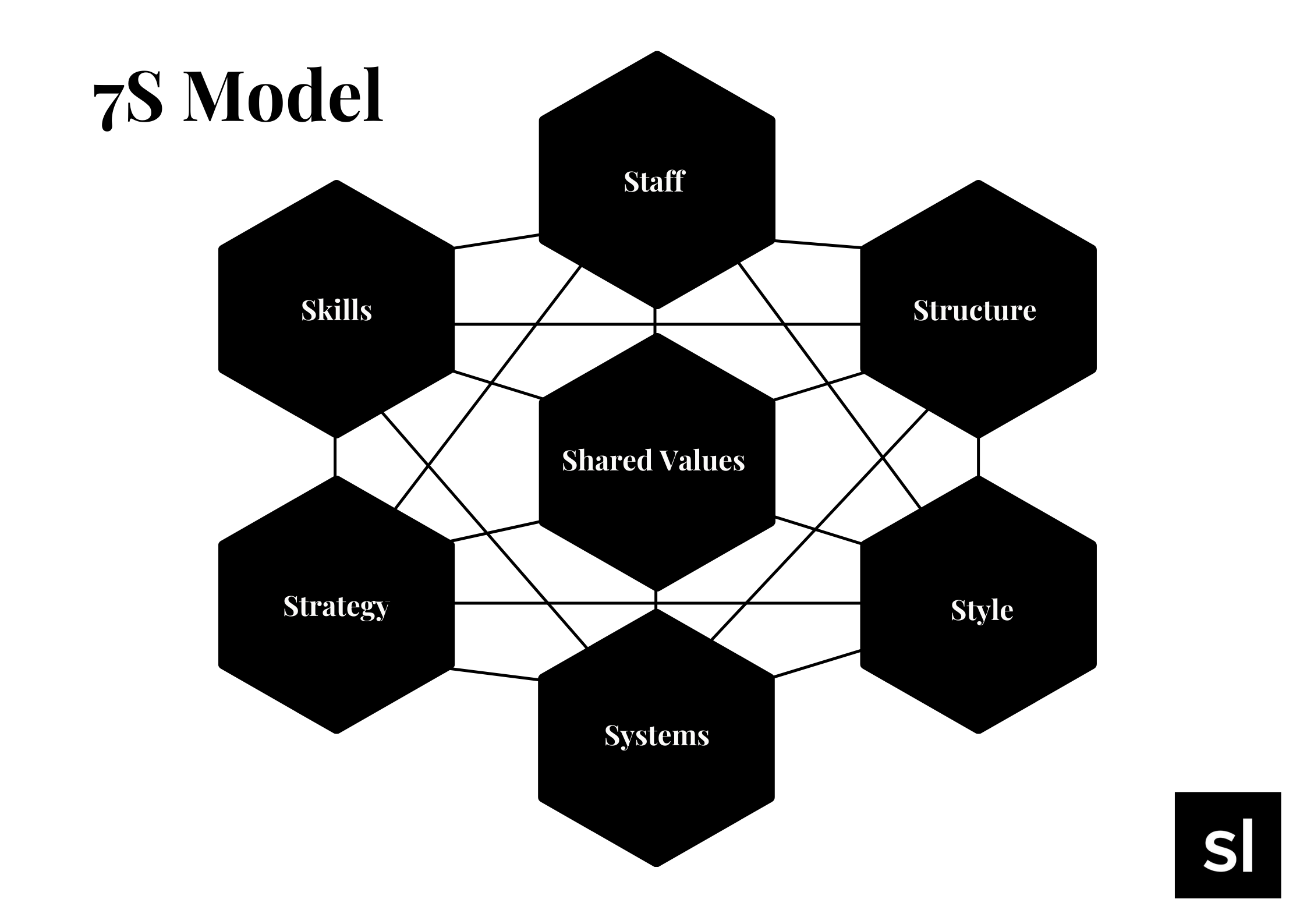
Shared values (which are at the heart of the model), skills (real skills and competencies), style (particularly, leadership style), and employees are all soft components (workers and talents in general).
Balanced Scorecard
Similar to OGSM, the initial version of the Balanced Scorecard was intended to link large picture strategic components with operational elements. This strategic planning framework looked at a company from four angles and suggested establishing objectives, measurements (KPIs), goals, and activities for each:
- Financial or stewardship management
- Stakeholders & Customers
- Internal Methodologies
- Learning and Growth or Organizational Capacity
The use of “strategy maps” – representations of strategic objectives divided across the four viewpoints – was introduced in the mid-1990s, resulting in an enhanced, second-generation model.
Following the mapping phase, the Balanced Scorecard framework is created by selecting only one or two measurements for each strategic goal, simplifying the process.
Later in the 1990s, a new iteration was created with the addition of “destination statements” and more functionality to strategic objectives. The framework’s designs are evolving to address flaws in the initial designs and to meet the needs of new business models.
Blue Ocean
The Blue Ocean strategy approach is based on Kim and Mauborgne’s idea of value innovation. Most approaches to corporate strategy are antithetical to value innovation, which advocates for firms to create new demand in underserved regions while keeping prices low.
This goal is achieved by removing the link between reduced prices and new demand utilizing the four-action framework:

The “strategy canvas,” a tool that helps firms differentiate their product from competitors, is one of the numerous strategic frameworks that Blue Ocean gives insight into.
The second phase of Blue Ocean focuses on developing a strategy based on four concepts (reconstructing market boundaries, big picture emphasis, going beyond existing supply and demand, and strategic sequencing) while managing across competitive lines.
Finally, Blue Ocean advises that the approach be implemented through tipping point leadership and a fair procedure while keeping in mind the political, cognitive, resource, and motivational barriers that might thwart the plan’s success.
Summing Up
Strategic frameworks are diagrams that outline corporate objectives and goals that might aid in the development of marketing strategies. They show you the way to success and must be addressed and updated regularly. Strategic frameworks should be evaluated regularly. This isn’t a “set it and forget it” approach.





